Table of Contents
Introduction
Galvanized pipe fittings are essential components in a wide variety of applications, from water systems to industrial machinery. The galvanization process, where steel pipes are coated with zinc, provides them with increased resistance to corrosion and rust. This makes them a popular choice for environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, and varying temperatures. However, while galvanized pipe fittings are resistant to rust for a time, they are not impervious. Over time, the zinc coating may degrade, leading to rust formation that can severely impact the performance and safety of the system.
Rust can cause blockages, leaks, and reduced pressure in piping systems, while also compromising the structural integrity of the pipes and fittings. If not addressed promptly, this can lead to costly repairs or replacements. Therefore, understanding how to avoid rust in galvanized pipe fittings is crucial for ensuring their longevity and reliability.
In this blog post, we will provide four key tips for preventing rust in galvanized pipe fittings, along with practical steps for maintaining them in optimal condition. This knowledge will help businesses avoid downtime and reduce maintenance costs associated with rust-related issues.
Understanding the Cause of Rust in Galvanized Pipe Fittings
Before discussing prevention, it’s important to understand why rust forms in galvanized pipe fittings. Galvanized pipes are coated with a layer of zinc to provide protection against corrosion. However, when the zinc layer begins to wear off or get damaged, the underlying steel is exposed to the elements, which can cause rust. The most common causes of this degradation include:
- Moisture Exposure: Extended exposure to moisture, particularly standing water, accelerates rust formation.
- Environmental Conditions: Exposure to salt, acids, or high humidity can break down the zinc layer, leading to corrosion.
- Physical Damage: Impact, abrasions, or installation errors can lead to the zinc layer getting scratched or worn off, allowing rust to develop.
Understanding these factors will help businesses take the necessary steps to prevent rust in their galvanized pipe fittings.
4 Key Tips to Prevent Rust in Galvanized Pipe Fittings
To prevent rust and ensure the longevity of galvanized pipe fittings, it’s important to follow best practices during installation, maintenance, and operation. Below are four key tips that can significantly reduce the risk of rusting in your galvanized pipe fittings.
1. Proper Installation to Minimize Exposure to Moisture

Proper installation is the first line of defense against rust in galvanized pipe fittings. Water is the primary contributor to rust formation, so minimizing exposure to moisture is essential.
Installation Tips:
- Use Gaskets and Seals: Ensure that gaskets and seals are properly installed to prevent water from seeping into pipe connections. This will prevent water accumulation, which can contribute to rust formation.
- Position Fittings Above Ground Level: For outdoor or exposed installations, ensure the fittings are installed above ground level, especially in areas prone to flooding or water accumulation.
- Ensure Proper Drainage: If the pipes are part of a drainage system, ensure that there is proper drainage so that water doesn’t stagnate in the pipes.
These installation practices can help minimize the risk of moisture exposure, which is a key contributor to rusting.
2. Regular Inspections and Maintenance

Routine inspections and regular maintenance are essential to detecting early signs of rust and preventing long-term damage. Regular checks allow you to catch issues before they escalate and to address minor concerns before they lead to larger problems.
Maintenance Tips:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect the pipe fittings for signs of corrosion, discoloration, or damage to the protective zinc coating. If any signs of rust are observed, address them immediately.
- Cleaning: Use non-abrasive methods to clean the galvanized pipe fittings. Harsh cleaning methods can damage the protective coating, making the pipes more susceptible to rust.
- Lubrication: Apply a thin coat of lubrication or rust-preventative oil to the fittings. This creates an additional barrier against moisture and environmental elements.
- Cleaning Filters and Drains: Ensure that filters and drains are regularly cleaned to prevent moisture accumulation in your pipes.
By staying on top of regular inspections and maintenance, you can significantly reduce the chances of rust forming on your galvanized pipe fittings.
3. Protective Coatings for Extended Protection
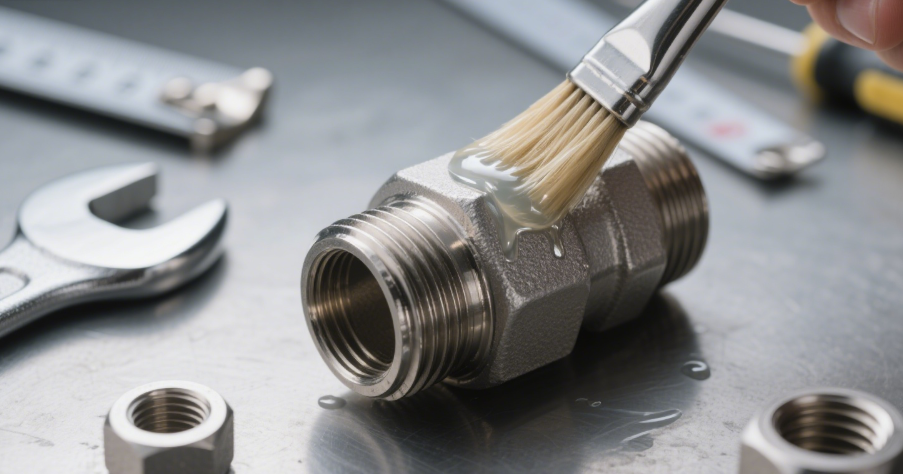

One of the most effective ways to prevent rust in galvanized pipe fittings is to apply an additional layer of protective coating over the galvanized surface. These coatings can help shield the zinc layer from damage caused by harsh chemicals or environmental factors.
Coating Options:
- Rust Inhibitors: Applying a rust inhibitor to galvanized pipe fittings provides extra protection against rust and corrosion. These inhibitors are typically applied as a spray and create a protective layer over the galvanized surface.
- Polyurethane Coatings: Polyurethane coatings offer a high level of protection against moisture and chemicals. These coatings can be applied to the fittings to protect them from the elements, especially in outdoor applications.
- Epoxy Coatings: Epoxy coatings are highly durable and effective in protecting galvanized pipe fittings from water, chemicals, and physical damage.
Comparison of Coating Options
| Coating Type | Benefits | Drawbacks | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rust Inhibitors | Protects against moisture, low cost | May require frequent reapplication | Low-maintenance environments |
| Polyurethane Coatings | Provides waterproof barrier | Can be expensive and time-consuming | Outdoor installations or wet areas |
| Epoxy Coatings | Strong chemical resistance | Hard to reapply once damaged | Heavy-duty industrial applications |
4. Control Environmental Factors

Environmental factors play a significant role in the rusting process. Humidity, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to chemicals can all accelerate the degradation of the zinc coating, leading to rust formation.
Environmental Tips:
- Ensure Adequate Ventilation: In areas with high humidity, ensure there is proper ventilation to allow moisture to dissipate and prevent condensation on the fittings.
- Temperature Control: Extreme temperature fluctuations can cause condensation on the surface of the galvanized pipe fittings, increasing the risk of rust. Where possible, keep temperatures moderate to prevent condensation.
- Limit Chemical Exposure: If possible, avoid exposing galvanized pipe fittings to harsh chemicals like acids, alkalis, and salts. These substances can break down the zinc layer and accelerate rust formation.
By controlling the environmental factors around galvanized pipe fittings, businesses can extend the lifespan of their fittings and reduce rusting risks.
Conclusion
Rust in galvanized pipe fittings can lead to significant issues, such as leaks, blockages, and system failure. However, by following proper installation procedures, conducting regular maintenance, applying protective coatings, and controlling environmental factors, businesses can reduce the risk of rust formation and ensure the long-term durability of their galvanized pipe fittings.
At Shandong Panel International Trade Co., Ltd., we offer high-quality galvanized pipe fittings designed to meet the highest industry standards. With our commitment to innovation and quality, our products provide reliable, long-lasting solutions for all your piping needs. Our experienced team is here to guide you through the process and help you find the right fittings for your project. Contact us today to receive a quote or to learn more about our offerings.
FAQ
How often should galvanized pipe fittings be inspected for rust?
We recommend conducting visual inspections at least twice a year or more frequently if the pipes are exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Can rust inhibitors be used on all galvanized pipe fittings?
Yes, rust inhibitors are safe to use on most galvanized pipe fittings and can provide an extra layer of protection.
What causes the zinc coating to break down on galvanized pipe fittings?
The zinc coating can break down due to physical damage, harsh chemicals, extreme temperatures, or prolonged exposure to moisture.
How can I identify rust on galvanized pipe fittings?
Look for reddish-brown discoloration or flakes on the surface of the fittings. Rust typically forms in areas where the zinc coating has been damaged or worn off.
Is it worth investing in protective coatings for galvanized pipe fittings?
Yes, protective coatings are a cost-effective way to enhance the longevity of galvanized pipe fittings, especially in high-risk environments where moisture and chemicals are prevalent.
What are the most common environmental factors that contribute to rust on galvanized pipe fittings?
Exposure to moisture, humidity, saltwater, extreme temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure are the primary environmental factors that accelerate rust formation on galvanized pipe fittings.
Can I repair rusted galvanized pipe fittings?
While it’s possible to repair minor rust damage with rust removers or by applying a new layer of zinc coating, severe rust damage may require replacement of the fittings to ensure the system remains safe and effective.
Do galvanized pipe fittings last longer than regular steel fittings?
Yes, this fittings are more resistant to rust and corrosion compared to regular steel fittings due to the protective zinc coating, which prolongs their lifespan in various environments.
What maintenance steps should be taken to prevent rust on galvanized pipe fittings?
Routine cleaning, visual inspections, applying rust inhibitors, and using protective coatings can help maintain the condition of galvanized pipe fittings and prevent rust. Ensure proper installation to avoid moisture buildup.
Can galvanized pipe fittings be used outdoors in all weather conditions?
The pipe fittings are suitable for outdoor use, but they should be protected from extreme weather conditions, especially saltwater or excessive humidity, which can hasten corrosion. Additional protective coatings may be necessary in harsher environments.