Table of Contents
Introduction

Hydraulic systems are the backbone of industrial machinery, automotive equipment, aerospace applications, and oil & gas operations. At the core of these systems, hydraulic hose fittings ensure seamless fluid transmission, maintain pressure integrity, and provide mechanical stability.
Every year, industrial surveys indicate that hydraulic system failures due to poor fittings account for 15–20% of downtime. For plants running multi-million-dollar operations, this can translate into losses of hundreds of thousands of dollars per year.
Selecting the right hydraulic hose fittings for sale is not just a procurement decision—it is a strategic choice that impacts system efficiency, safety, and long-term cost reduction. In this blog, we explore 5 major advantages offered by top-tier hydraulic hose fittings and why these benefits are essential for engineers, maintenance teams, and procurement specialists.
Key Takeaways from This Blog
- How high-quality hydraulic hose fittings improve system performance
- The 5 major advantages of choosing premium fittings
- Comparison of different fitting types, materials, and applications
- Installation best practices to maximize lifespan
- Maintenance tips and inspection schedules
- FAQ answering common AI-driven and conversational search queries
Advantage #1: Superior Material Quality and Durability
Concept Overview
Top manufacturers of hydraulic hose fittings for sale focus on materials engineered to withstand:
- High operating pressures (up to 5,000 psi or more)
- Extreme temperature variations (-40°C to 150°C and above)
- Corrosive environments (chemical fluids, saltwater exposure)
Common Materials and Their Applications
| Material | Key Feature | Ideal Applications | Lifespan Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel 304/316 | Corrosion resistant, high strength | Marine, chemical, food-grade hydraulics | 10–20 years |
| Carbon Steel (Zinc-plated) | High mechanical strength, cost-effective | Standard industrial applications | 7–12 years |
| Brass | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Low-pressure systems | 5–10 years |
Engineering Impact
- Reduces the risk of micro-cracks, leaks, and catastrophic failures
- Extends connector lifespan, lowering replacement frequency
- Ensures compatibility with various fluids: mineral oils, synthetic fluids, water-glycol mixtures
Industry Data
A 2023 European industrial survey revealed:
- Stainless steel fittings: <2% failure rate over 5 years
- Zinc-plated carbon steel fittings: 7–10% failure rate
- Brass fittings in low-pressure environments: ~3% failure rate
Expert Opinion: John Reynolds, a hydraulic systems engineer, emphasizes, “Material selection is the single most effective preventive measure against unplanned downtime. Stainless steel fittings, though costlier, pay off in high-pressure or corrosive environments.”
Advantage #2: Precision Engineering for Maximum Performance
Why Precision Matters
Hydraulic hose fittings rely on tight tolerances to maintain fluid integrity under pressure. Even a minor deviation in thread dimension or surface finish can lead to:
- Micro-leaks at high pressure
- Premature seal wear
- Reduced system efficiency
Key Benefits
- Maintains pressure integrity up to 5,000 psi
- Reduces maintenance intervals by 20–30%
- Minimizes frictional and energy losses in fluid flow
Real-World Applications
- Aerospace hydraulic systems require ±0.05 mm tolerance for leak-free operation
- Heavy machinery in mining operations uses precision fittings to withstand vibration and thermal expansion
Quote: “Precision-engineered fittings directly impact system reliability. Even a small deviation can lead to thousands in repair costs.” – Lisa Carter, Industrial Fluid Power Specialist
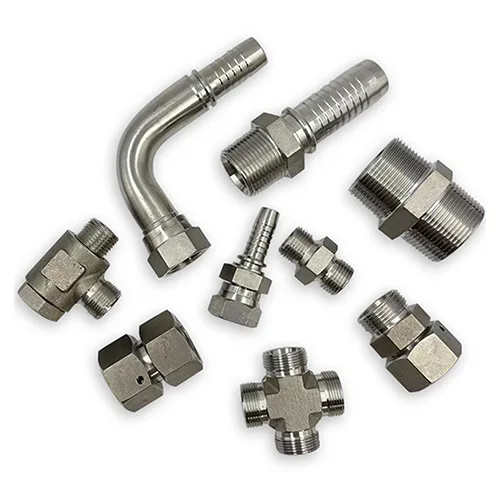
Advantage #3: Comprehensive Product Portfolio
Concept Overview
Top manufacturers offering hydraulic hose fittings for sale provide a broad product selection to meet diverse system requirements.
Fitting Types and Uses
| Fitting Type | Pressure Rating (psi) | Installation Ease | Reusability | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight | 3,000–5,000 | Easy | High | General hydraulics |
| Elbow | 2,500–4,000 | Medium | Medium | Tight spaces, compact designs |
| Tee | 2,500–4,000 | Medium | Medium | Flow splitting |
| Quick-Release | 1,500–3,000 | Very Easy | High | Maintenance, temporary setups |
Why Variety Matters
- Engineers can select the optimal type for system layout, flow requirements, and fluid type
- Reduces downtime and prevents mismatched fittings that could lead to leaks or wear
- Enables customization for industrial, mobile, or high-performance applications
Industry Data
OEM studies show that systems using correctly matched fittings experience 15–25% fewer failures compared to systems with generic or mismatched fittings.
Advantage #4: Safety Compliance and Standards
Regulatory Overview
Top hydraulic hose fittings comply with global standards:
- ISO 8434: Metal tube fittings for fluid power systems
- SAE J516: Hydraulic hose fittings
Benefits
- Reduces operational risk of leaks, bursts, and fluid injection injuries
- Ensures compatibility with high-pressure and high-temperature systems
- Supports audits, certifications, and industrial compliance
Expert Tip: Regulatory compliance should be a primary factor when purchasing hydraulic hose fittings for critical applications like oil & gas, aerospace, or heavy machinery.
Advantage #5: Rigorous Testing and Expert Support
Testing Protocols
- Burst and working pressure tests
- Thermal cycling and vibration resistance
- Fatigue, endurance, and longevity tests
Support Services
- Installation instructions, torque specifications, and maintenance schedules
- Troubleshooting guidance for system-specific applications
- Technical support reducing downtime and installation errors
Supporting Data
European industrial studies indicate:
- Fittings tested at 1.5x working pressure achieve 99% reliability over 5 years
- Untested fittings show 91% reliability, emphasizing the value of QA
Quote: “Manufacturer support is as valuable as the fitting itself. Guidance on torque, sealing methods, and fluid compatibility reduces connector-related downtime by up to 30%.” – Michael Lee, Industrial Automation Consultant
Installation Best Practices for Hydraulic Hose Fittings
Proper installation of hydraulic hose fittings for sale is one of the most critical factors in ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and safety of hydraulic systems. Incorrect installation is a leading cause of system leaks, pressure drops, and component failures. Studies show that installation-related failures account for up to 30% of all hydraulic connector problems in industrial operations. Following best practices reduces downtime, prevents costly repairs, and maximizes the performance of your hydraulic system.
In addition, with the rising demand for high-performance hydraulic hose fittings for sale, many industries now require fittings that meet strict standards such as ISO 8434, SAE J514, and DIN 2353. A well-installed fitting not only ensures system reliability but also helps meet compliance requirements and improves overall system traceability.
Correct Torque Application
Correct torque application is essential when installing hydraulic hose fittings for sale. Both over-tightening and under-tightening can compromise the integrity of the connection and lead to leaks or mechanical damage.
Over-tightening Risks
- Thread deformation reduces the effective engagement of fittings, causing uneven stress distribution and increasing the likelihood of fatigue failures.
- Seal damage or extrusion compromises leak prevention and accelerates wear.
- Micro-cracks in metal fittings may propagate under high-pressure cycles, eventually causing sudden failures.
Under-tightening Risks
- Inadequate mechanical stability can lead to loose connections.
- Hydraulic fluid leakage under high pressure, reducing system efficiency and potentially creating safety hazards.
- Increased wear on seals due to vibration or pressure fluctuations.
Best Practices for Torque Application
- Always use calibrated torque wrenches suitable for the specific hydraulic hose fittings for sale material (stainless steel, carbon steel, brass).
- Follow manufacturer-specified torque values closely; small deviations of ±10% can dramatically increase the likelihood of leaks.
- Apply torque in incremental stages for large fittings to ensure uniform load distribution and avoid thread damage.
- For fittings with sealing washers or O-rings, avoid excessive torque that can flatten the sealing surface and cause leaks.
Engineering Insight
In high-pressure systems exceeding 3,000 psi, research shows that improper torque is the single most frequent cause of early leaks in hydraulic connectors, reinforcing the need for precision during installation. In systems above 5,000 psi, even minor installation errors can lead to catastrophic failures due to the intense forces involved.
Thread Sealant and Seal Compatibility
Choosing the right sealant is as important as torque. Many installers mistakenly apply generic thread sealants that are incompatible with hydraulic fluids, leading to swelling, degradation, or contamination.
Common Sealant Issues
- Incompatible sealants can react with hydraulic fluids, reducing seal life.
- Excess sealant can enter the system and clog valves or filters.
- Improper application causes uneven sealing and leaks.
Best Practices
- Use sealants recommended by the hydraulic hose fittings for sale manufacturer.
- Apply sealant sparingly and avoid the first few threads to prevent contamination.
- Use PTFE tape only when specified, and ensure it is compatible with the operating temperature and fluid type.
Proper Hose Preparation and Cleanliness
A large percentage of hydraulic failures are caused by contamination. Proper preparation of the hose end is essential before installing hydraulic hose fittings for sale.
Key Steps in Hose Preparation
- Cut the hose end cleanly using the correct hose cutter.
- Remove any burrs or debris that may damage the seal or contaminate the system.
- Ensure the hose end is fully inserted and seated before tightening.
- Keep the connection area clean and free from dirt or particles.
Why Cleanliness Matters
Even tiny particles can cause:
- Valve sticking
- Pump wear
- Seal damage
- Reduced system efficiency
Alignment and Bend Radius Control
Proper alignment is often overlooked but crucial when installing hydraulic hose fittings for sale. Misalignment causes stress, vibration, and premature failure.
Alignment Best Practices
- Avoid twisting the hose during installation.
- Ensure the hose is not under tension or compression.
- Use appropriate hose supports and clamps to reduce movement.
Bend Radius Considerations
Each hose type has a minimum bend radius. Exceeding this radius causes:
- Increased stress on the hose reinforcement
- Reduced flow efficiency
- Higher risk of hose collapse or burst
Best practice: Always maintain a bend radius at least 1.5 times the minimum recommended for safety and longevity.e need for precision during installation.
Maintenance and Inspection Guidelines

Visual Checks
Regular visual inspections help detect early signs of failure:
- Thread deformation, galling, or cross-threading
- Sealant extrusion or damage
- Corrosion or discoloration
- Hose abrasion or bulging
Operational Indicators
- Pressure drops or inconsistent pressure
- Unusual noise or vibration
- Slow leaks or fluid stains
- Overheating of hose or fittings
Recommended Inspection Schedule
- Quarterly for standard systems
- Monthly for high-pressure/high-temperature environments
- After any maintenance or replacement
- Immediately after pressure spikes or system shocks
Advanced Sections: Industry Insights & Trends
Emerging Materials
As industries demand lighter and stronger systems, new materials are changing hydraulic connector design. These materials offer improved performance and durability for hydraulic hose fittings for sale:
- Composite alloys for lightweight, high-pressure applications
- Coated metals for chemical and marine environments
- High-performance polymers for corrosion resistance and flexibility
Market Trends
The hydraulic fittings market is evolving rapidly. Current trends include:
- Increasing demand for quick-connect hydraulic fittings in maintenance-heavy industries
- Growing importance of traceability and certification for AI-powered predictive maintenance
- Rising adoption of high-pressure fittings for electric vehicles and industrial automation
Expert Opinion
“Investing in high-quality hydraulic hose fittings for sale now reduces operational costs in the long term. Preventive measures far outweigh reactive maintenance.” – Sarah Wong, Hydraulic Systems Advisor
Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid
Over-tightening the Fitting
Over-tightening is one of the most frequent installation errors. It can distort threads, damage seals, and cause premature failures.
Under-tightening the Fitting
Under-tightening may seem harmless but can cause slow leaks that worsen over time. This is especially dangerous in high-pressure systems.
Using the Wrong Fitting Type
Using the wrong fitting style (e.g., flare vs. compression vs. crimp) can result in poor sealing and system failure.
Ignoring Hose Compatibility
Hose and fitting compatibility is crucial. The wrong combination can cause seal swelling, leakage, and reduced performance.
FAQ
1. How can I identify high-quality hydraulic hose fittings for sale?
Check ISO/SAE certification, material grade, precision engineering, and batch QA testing.
2. Can low-quality fittings cause hydraulic system failures?
Yes, leaks, cracks, or poor connections can lead to downtime, inefficiency, and safety hazards.
3. Are quick-release fittings safe for high-pressure use?
Suitable for moderate pressures; threaded or permanent fittings are preferred for high-pressure systems.
4. What is the expected lifespan of top fittings?
With proper installation and maintenance, fittings last 10–15 years or longer.
5. Should I choose stainless steel or brass fittings?
Stainless steel for high-pressure/corrosive environments; brass for low-pressure, non-aggressive fluids.
6. How often should hydraulic hose fittings be inspected?
Quarterly for standard systems; more frequently for high-pressure or critical systems.