Table of Contents
Introduction

Hydraulic systems are essential for modern machinery, from industrial equipment to mobile machinery, agricultural vehicles, and construction equipment. Choosing the correct SAE 6 hydraulic fittings is critical—not only for operational efficiency but also for system safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Incorrect selection can cause:
- Leaks or pressure drops
- Premature component failure
- Increased maintenance costs and downtime
In this guide, you will learn:
- 3 key tips for selecting SAE 6 hydraulic fittings
- How to match fittings to system pressure, material, and seal requirements
- Comparisons with other hydraulic fitting standards
- Real-world applications across industries
- Maintenance best practices and troubleshooting techniques
- Market trends, technological innovations, and expert insights
This comprehensive guide is designed for engineers, maintenance professionals, and anyone involved in hydraulic system design or operation.
Understanding SAE 6 Hydraulic Fittings
What Are SAE 6 Hydraulic Fittings?
SAE 6 hydraulic fittings are standardized connectors used in medium- to high-pressure hydraulic systems. “SAE 6” refers to a 3/8-inch nominal size according to SAE J514 and ISO 8434-2 standards.
They are designed to provide:
- Leak-free connections
- Compatibility with hoses, tubes, and other hydraulic components
- Reliability under industrial, mobile, and marine applications
Industry Insight: SAE 6 fittings make up over 25% of medium-sized hydraulic system connections due to their versatility and standardized design (Hydraulic Engineering Today, 2023).
Key Factors in Fitting Selection
Selecting the wrong SAE 6 hydraulic fitting can result in:
- Hydraulic leaks leading to fluid loss
- Reduced system pressure and efficiency
- Premature system failure
Expert Opinion: John Ellis, a hydraulic systems engineer, states:
“Even a minor misfit in hydraulic connectors can reduce efficiency by up to 15% and significantly increase maintenance costs.”
Tip 1: Match SAE 6 Hydraulic Fittings to Pressure Ratings

Understanding Pressure Ratings
Every SAE 6 hydraulic fitting is rated for a maximum working pressure. Choosing the correct rating ensures system safety and performance. Common pressure ratings include:
- Standard: up to 3000 psi (207 bar)
- Heavy-duty: up to 4500 psi (310 bar)
- Stainless steel reinforced: up to 5000 psi (345 bar)
Systems experiencing fluctuating pressures should have a 25–30% safety margin above peak operating pressures.
Heavy-duty and stainless steel SAE 6 hydraulic fittings are ideal for industrial machinery, construction equipment, and high-load mobile systems.
Table 1: SAE 6 Hydraulic Fittings Pressure Ratings
| Fitting Type | Max Pressure | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Standard SAE 6 | 3000 psi | General machinery, light industrial |
| Heavy-Duty SAE 6 | 4500 psi | Construction and manufacturing equipment |
| Stainless Steel SAE 6 | 5000 psi | Corrosive or extreme environments |
Industry Insight:
A 2022 North American hydraulic systems survey showed that 42% of medium-duty system failures were caused by under-rated fittings, emphasizing the importance of proper SAE 6 hydraulic fittings pressure selection.
Expert Tip:
“Always verify pressure ratings against the peak operating pressures, especially in mobile or high-vibration environments. Overlooking this can cause leaks or catastrophic system failures.” – John Ellis, Hydraulic Systems Engineerthe importance of pressure selection.
Tip 2: Choose the Right Material
Material Options for SAE 6 Hydraulic Fittings
The choice of material significantly affects durability, corrosion resistance, and overall system performance. Common options include:
- Carbon Steel: Strong, affordable, suitable for general industrial applications
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, ideal for marine, outdoor, and chemical applications
- Brass or Alloy: Used in lower-pressure systems or for specific fluids
Industry Data:
Stainless steel SAE 6 hydraulic fittings last up to 40% longer than carbon steel fittings in high-moisture or corrosive environments (Industrial Hydraulic Journal, 2023).
Matching Material to Application
| Material Type | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High | Low | Industrial machinery |
| Stainless Steel | High | Very High | Marine, outdoor, aggressive fluids |
| Brass/Alloy | Medium | Medium | Chemical fluids, low-pressure systems |
Expert Insight:
“Material selection is not just about strength—it’s about compatibility with the hydraulic fluid, operating environment, and maintenance cycles. Using stainless steel SAE 6 fittings in a marine crane dramatically reduces replacement costs.” – Maria Gonzales, Hydraulic Maintenance Specialist
Tip 3: Consider Sealing and Connection Types
TThread and Seal Options
Proper sealing is essential to prevent leaks and maintain system pressure. Common options for SAE 6 hydraulic fittings include:
- O-ring Face Seal (ORFS): Leak-proof under high pressure, ideal for mobile and industrial hydraulics
- Flared fittings: Easy to install, moderate-pressure applications
- Straight-thread fittings: Require sealant or Teflon tape, suitable for low-pressure systems
Matching Fittings to System Requirements
- High-pressure mobile hydraulics: ORFS or heavy-duty flared fittings
- Low-pressure industrial systems: Standard flared or straight-thread fittings
Maintenance Tip:
Inspect threads and O-rings before installation, and apply the correct torque to prevent leaks, thread stripping, or seal damage.
Comparing SAE 6 Hydraulic Fittings with Other Standards
| Feature | SAE 6 Fittings | JIC 37° Fittings | Metric Hydraulic Fittings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thread Standard | SAE J514 | 37° flare | ISO 8434 |
| Size | 3/8 inch | 3/8 inch | 10 mm |
| Max Pressure | 3000–5000 psi | 3000–6000 psi | 250–350 bar |
| Sealing Type | Flare, ORFS | Flare, ORFS | O-ring or cone |
| Application Flexibility | High | High | Medium |
Takeaway: SAE 6 fittings are versatile, but pressure rating, material, and sealing type selection are critical for reliability.
Real-World Applications

Industrial Machinery
- Presses, injection molding machines, and CNC equipment
- Provide reliability under constant load, easy maintenance access
Mobile and Construction Equipment
- Excavators, loaders, agricultural machinery
- Resilient to vibration and harsh conditions, leak-proof connections
Marine and Offshore Applications
- Stainless steel SAE 6 fittings resist saltwater corrosion
- Extend service life under aggressive environmental conditions
Case Study: A European port replaced standard fittings with stainless steel SAE 6 in crane hydraulics. Result: 28% downtime reduction, 15% annual maintenance cost saving.
Advanced Design Considerations
Hose and Tube Compatibility
- SAE 6 fittings are compatible with standard hoses and tubing
- Check inside diameter (ID) and outside diameter (OD) for proper fit
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
- Carbon steel: tolerates most industrial oils, moderate temperature
- Stainless steel: tolerates higher temperatures and aggressive fluids
Expert Insight: Thermal cycling can degrade seals. For high-temperature systems, ORFS fittings with Viton O-rings are recommended.
Common Installation Mistakes
- Over-tightening: Can strip threads or damage O-rings
- Incorrect torque: Leads to leaks and pressure drops
- Wrong seal selection: Using low-temp O-rings in high-heat systems
- Improper material choice: Leads to corrosion or premature failure
Maintenance and Best Practices
- Inspect every 6–12 months or after high-stress operation
- Use calibrated torque wrenches
- Clean and flush systems regularly to remove debris
- Store spare fittings in dry, clean environments
Expert Tip: Regular inspections and preventive maintenance can extend fitting service life by 50% or more.
Market Trends and Industry Insights
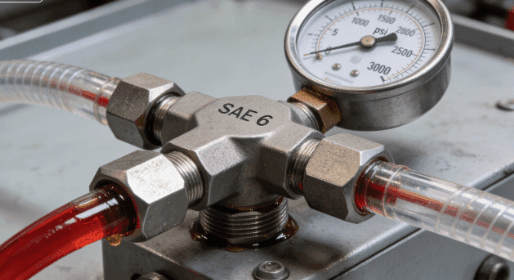
- Market Size: Hydraulic fittings market projected to reach $12 billion by 2030, CAGR 6.5%
- Technological Advances: IoT-enabled fittings for predictive maintenance
- Sustainability: Eco-friendly coatings and corrosion-resistant materials
- Adoption Drivers: Automation, labor cost pressures, industrial safety regulations
Conclusion
Correct SAE 6 hydraulic fitting selection ensures:
- Leak-free, safe operation
- Optimal hydraulic performance
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Increased system longevity
By carefully evaluating pressure ratings, materials, sealing types, and environmental conditions, engineers and maintenance teams can maximize system efficiency, prevent costly failures, and ensure reliability across industrial, mobile, and marine hydraulic applications.
FAQ
Q1: Can SAE 6 fittings handle high-pressure systems?
A: Yes, standard fittings up to 3000 psi; heavy-duty/stainless up to 5000 psi.
Q2: How to prevent leaks?
A: Use correct O-rings, inspect threads, and follow torque specs.
Q3: Are SAE 6 and JIC fittings interchangeable?
A: Not always; JIC uses a 37° flare standard.
Q4: Best material for outdoor applications?
A: Stainless steel for corrosion resistance.
Q5: Inspection frequency?
A: Every 6–12 months, or more frequently in high-stress systems.
Q6: What is the difference between SAE 6 ORFS and flared fittings?
A: ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal) fittings provide leak-free performance under high pressure, while flared fittings are easier to install but handle moderate pressure levels.
Q7: Can SAE 6 fittings be reused after disassembly?
A: Generally, reusable if threads and O-rings are in good condition, but seals often require replacement to ensure leak-free performance.
Q8: How do I choose the right SAE 6 fitting for a hydraulic hose?
A: Match the fitting size and pressure rating to the hose specifications, consider the type of fluid, and select compatible materials to prevent corrosion or wear.
Q9: Are SAE 6 hydraulic fittings compatible with synthetic hydraulic fluids?
A: Most carbon steel and stainless steel SAE 6 fittings are compatible, but check the O-ring material (e.g., Viton or NBR) for chemical resistance to the specific synthetic fluid.
Q10: How can I identify a high-quality SAE 6 hydraulic fitting?
A: Look for certifications (SAE J514 or ISO 8434-2), precise machining, smooth threads, and durable materials such as stainless steel or high-grade carbon steel.