Table of Contents
Introduction

316 ss pipe fittings are an essential component in industrial piping systems due to their high corrosion resistance, durability, and ability to withstand extreme conditions. They are widely used in chemical plants, marine applications, food processing, pharmaceutical industries, and high-purity water systems.
For beginners, improper handling, selection, or installation can lead to serious failures, costly downtime, or even safety hazards. Understanding common mistakes and implementing best practices is crucial for ensuring long-term reliability and safety of pipelines. This article explores five risky mistakes, supported by examples, tables, and practical tips to avoid them.
Mistake 1: Using the Wrong Type of 316 SS Pipe Fittings
Why Selection Matters
Not all 316 ss pipe fittings are suitable for every application. Using standard fittings in aggressive environments, like saltwater or chemical exposure, can accelerate corrosion, reduce service life, and compromise system safety.
Types of 316 SS Pipe Fittings and Their Applications
Elbows: Designed to change the flow direction, available in 45° and 90° angles. Ideal for smooth flow transitions in complex piping layouts.
Tees: Split pipelines efficiently and allow branch connections. Common in water distribution and chemical transport systems.
Reducers: Allow for pipe diameter transitions, ensuring smooth fluid flow and minimal pressure loss.
Couplings: Join two pipe ends securely, critical for maintenance and system extensions.
Flanges: Provide leak-proof connections between pipes or equipment. Essential in high-pressure applications.
Key Considerations for Proper Selection
- Verify material certifications and compliance with ASTM A182 or A403 standards.
- Consider the chemical compatibility of fittings with fluids being transported.
- Assess temperature and pressure ratings for specific application conditions.
Real-World Insight: According to Dr. Angela Thompson, a piping systems consultant:
“The choice of fittings at the design stage defines the performance baseline. Selecting an incompatible fitting can result in early corrosion and costly replacement.”
Mistake 2: Improper Installation Techniques
Threaded vs Welded Fittings
Threaded Fittings: Convenient for assembly and disassembly, but over-tightening can strip threads and reduce sealing performance.
Welded Fittings: Provide stronger, leak-proof connections but require precise alignment and skilled welding to prevent stress points.
Common Installation Errors by Beginners
- Misaligned flanges or weld joints
- Excessive torque on threaded fittings
- Incorrect weld angles causing stress concentration
- Neglecting gaskets or sealants in flanged joints
Best Practices for Proper Installation
- Use torque wrenches and follow manufacturer specifications for threaded fittings.
- Ensure alignment using laser or mechanical alignment tools before welding.
- Maintain consistent welding temperatures to avoid weakening the stainless steel structure.
- Inspect joints visually and, if possible, with NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) methods.
Installation Case Study
A chemical plant experienced frequent leaks in a newly installed piping section. Investigations revealed threaded fittings were over-tightened, causing microfractures. Correcting torque settings and retraining staff resolved the issue.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Compatibility with Fluids and Environmental Conditions
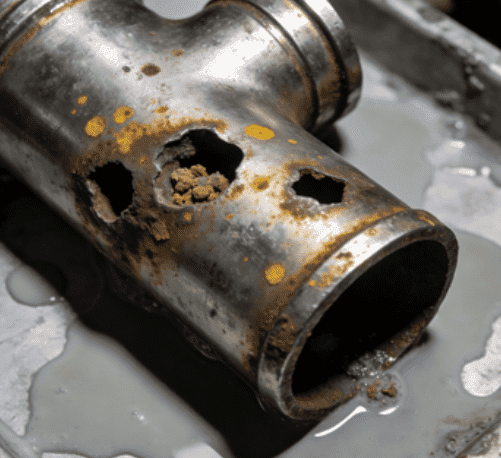

Chemical Resistance Misconceptions
316 SS is known for excellent corrosion resistance, but beginners often assume it is universally resistant. Chlorides, acids, and high-concentration salts can cause pitting or crevice corrosion if the fittings are not selected correctly.
Environmental Factors That Affect 316 SS Pipe Fittings
- Temperature extremes: High heat can reduce corrosion resistance.
- Pressure variations: High-pressure environments require precise wall thickness and grade selection.
- Saline exposure: Coastal or marine applications require careful monitoring for pitting corrosion.
Recommendations for Ensuring Compatibility
- Verify that 316 SS grade is appropriate for specific chemical exposure.
- Use protective coatings or passivation treatments when necessary.
- Conduct stress analysis if fittings will be exposed to dynamic pressure or vibration.
Mistake 4: Neglecting Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Importance of Routine Checks
Even high-quality 316 ss pipe fittings degrade over time if not maintained. Regular inspections detect corrosion, leaks, or mechanical wear before they escalate into major failures.
Typical Inspection Steps
- Visual check for discoloration, rust, or pitting
- Torque verification for threaded joints
- Weld inspection for cracks or defects
- Check for leaks under operational conditions
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
- Apply anti-corrosion sprays or passivation solutions on exposed joints.
- Schedule inspections every 6–12 months or after extreme environmental exposure.
- Maintain a maintenance log for each pipeline section, noting repairs, replacements, and inspection dates.
Example: An industrial water system reported a 20% reduction in leakage incidents after implementing a biannual inspection program for all 316 SS fittings.
Mistake 5: Overlooking Proper Storage and Handling

Risks of Improper Storage
Scratches, dents, and contamination during storage can compromise the protective chromium oxide layer on 316 SS pipe fittings, leading to localized corrosion.
Safe Handling and Storage Practices
- Store fittings on clean racks or pallets, off the ground.
- Avoid direct contact with abrasive surfaces.
- Keep fittings in a dry, ventilated area away from corrosive materials.
- Use protective packaging for long-term storage.
Real-World Example
A factory discovered pitting corrosion on new fittings that were stacked directly on a concrete floor. By switching to elevated storage racks and protective covers, corrosion incidents were eliminated.
316 SS Pipe Fittings Specifications Table
| Fitting Type | Common Application | Material Grade | Connection Type | Max Operating Pressure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elbow 90° | Change in direction | 316 SS | Threaded/Weld | 3000 PSI |
| Tee | Branching lines | 316 SS | Welded | 2500 PSI |
| Reducer | Diameter transition | 316 SS | Welded/Thread | 2800 PSI |
| Coupling | Join two pipes | 316 SS | Threaded | 3000 PSI |
| Flange | Connection and sealing | 316 SS | Welded/Bolted | 3200 PSI |
This table serves as a quick reference to compare fitting types, typical applications, connection methods, and maximum operating pressures for 316 SS pipe fittings.
Expert Tips for Beginners
Material Verification
Always check that fittings are genuine 316 SS and meet ASTM or ISO standards. Counterfeit or lower-grade stainless steel may fail prematurely.
Using the Right Installation Tools
Employ torque wrenches, alignment jigs, and proper welding equipment to ensure joints are secure and correctly aligned.
Scheduled Maintenance
Even corrosion-resistant fittings require cleaning, inspection, and monitoring for wear and damage.
Environmental Suitability
Consider temperature, chemical exposure, and pressure ratings before installation to prevent premature degradation.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Raw Material Variability
Logs and billets can differ in composition, affecting fitting quality. Only use certified 316 SS material from reputable suppliers.
Equipment Downtime
Preventive maintenance, spare part inventory, and staff training reduce unexpected stoppages.
Environmental Hazards
High humidity, airborne salts, and chemicals can accelerate corrosion. Adequate ventilation and protective measures are essential.
FAQ
Q: Can 316 ss pipe fittings handle saltwater environments?
A: Yes, but ensure they are free of scratches and passivated properly for long-term corrosion resistance.
Q: Are threaded fittings suitable for high-pressure pipelines?
A: Only for moderate pressures; welded or flanged fittings are preferred for high-pressure applications.
Q: How often should 316 SS pipe fittings be inspected?
A: Every 6–12 months or after extreme operating conditions.
Q: Is 316 SS suitable for high-temperature applications?
A: It performs well under moderate heat. Check manufacturer ratings for specific high-temperature limits.
Q: How should 316 SS fittings be stored for long periods?
A: Dry, ventilated areas, off the floor, with protective packaging to prevent scratches or contamination.
Conclusion
Beginners frequently make errors in selection, installation, maintenance, and handling of 316 SS pipe fittings. These mistakes can lead to leaks, corrosion, and costly downtime. By understanding proper selection, installation, maintenance, and storage practices, beginners can ensure reliable, safe, and long-lasting performance of 316 SS piping systems. Structured training, regular inspections, and attention to environmental compatibility are key to mastering the safe use of these critical components.