Key Takeaways
- Understand why connection choice matters for system reliability and safety
- Learn the technical differences between ss pipe coupling and flange
- Discover procurement-focused criteria like cost, maintenance, and installation speed
- See a detailed comparison table with real-world decision factors
- Get practical guidance on when to choose coupling or flange
- Learn how to match connection type to pressure, temperature, and pipe diameter
Table of Contents
Introduction
In piping systems, the connection method is not just a technical detail—it is a strategic decision that impacts safety, cost, downtime, and long-term maintenance. A wrong choice can lead to leakage, unplanned shutdowns, and huge repair expenses. For procurement managers and engineers, understanding the difference between ss pipe coupling and flange is essential to make the most cost-effective and reliable selection. In this blog, we compare both connection types through real-world scenarios, industry standards, and practical procurement considerations. By the end, you will clearly know which option is the best fit for your project.
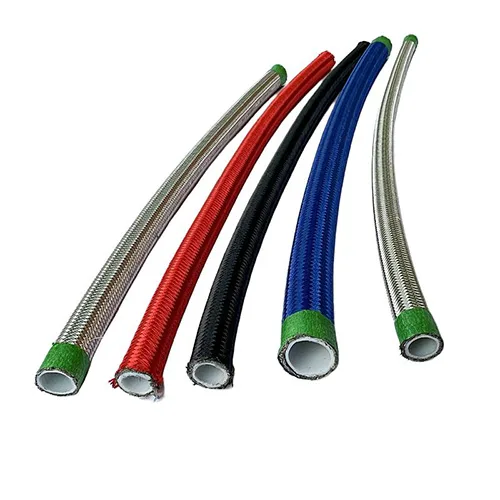
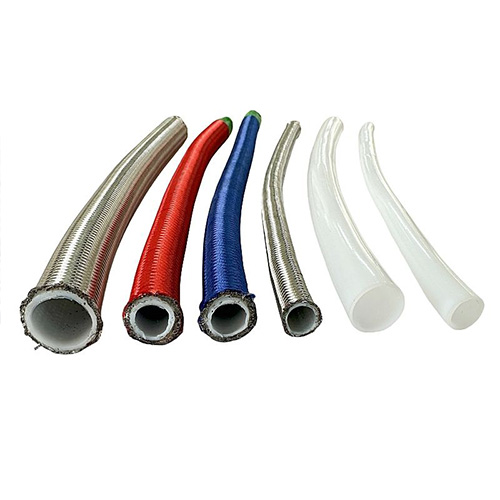
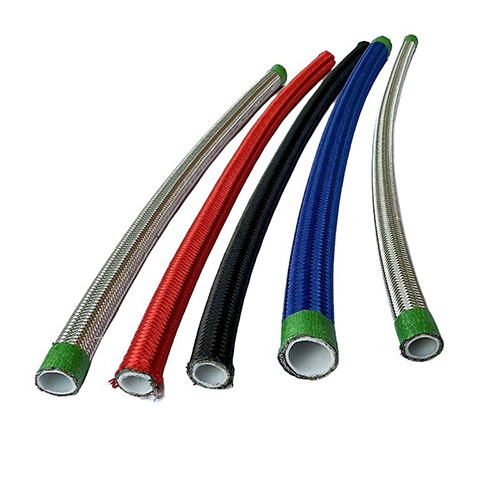
What Is an ss pipe coupling?
An ss pipe coupling is a connector used to join two stainless steel pipes without welding. It uses mechanical compression, threads, or a sleeve design to create a tight seal. Couplings are widely used in industrial water systems, chemical pipelines, HVAC, and food processing lines due to their fast installation and lower cost.
Core concept of coupling
A coupling provides a compact connection method, ideal for tight spaces and modular piping systems. Its reliability depends heavily on the sealing material, installation quality, and proper torque.
Typical structure
Most couplings consist of a sleeve body, gasket, and bolts. The gasket material is critical, and different applications require different materials such as EPDM, PTFE, or NBR.
What Is a Flange Connection?
A flange connection uses two matching plates that are bolted together with a gasket between them. Flanges are common in high-pressure, high-temperature systems, and in industrial applications where frequent disassembly is required.
Core concept of flange
Flanges provide a strong mechanical connection and are suitable for large diameter pipes. They allow easy inspection and replacement of valves or sections of piping.
Typical structure
Flanges include the flange body, gasket, bolts, and nuts. Flange standards like ANSI/ASME B16.5 and ISO 7005 define dimensions, pressure classes, and tolerances.
Why Both Methods Still Dominate Modern Industry
Despite the emergence of advanced joining technologies, ss pipe coupling and flange remain the most widely used due to:
- Proven reliability over decades
- Strong global supply chain and standardized specifications
- High compatibility with existing piping systems
- Easy procurement and replacement
Installation Complexity: Coupling vs Flange
Why coupling installation is faster
Couplings require minimal tools and can often be installed by general maintenance staff. For many projects, coupling reduces installation time by up to 30% compared to flanges.
Why flange installation is more complex
Flange installation often requires welding, precise alignment, and torque control. For high-pressure systems, flange installation must be performed under strict quality control to avoid leakage and ensure safety.
Cost Comparison: Not Just Material Price
Coupling cost advantage
Couplings generally have lower material and labor cost. They are often the best option when budget control is the priority.
Flange cost advantage in long-term
Flanges may cost more upfront, but in systems requiring frequent maintenance or inspection, flange connections can reduce downtime cost, especially in large industrial plants.
Reliability Comparison: How to Evaluate Long-Term Performance

Coupling reliability depends on installation quality
Couplings can be highly reliable if installed correctly. However, if the gasket is incompatible or the bolts are unevenly tightened, leakage can occur.
Flange reliability is highly stable under extreme conditions
Flanges are more suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature environments. The sealing performance is more predictable when proper torque and gasket material are used.
Sealing Performance: The Most Critical Factor
Coupling sealing principle
Couplings rely on compression and gasket elasticity. The sealing strength depends on correct torque and gasket material compatibility.
Flange sealing principle
Flanges seal by compressing the gasket between two flat surfaces. With proper torque and material selection, flanges can provide extremely stable sealing performance.
Maintenance and Inspection: Which Is Easier?
Coupling maintenance
Couplings are easier to replace and often require less downtime. In small piping systems, couplings are the most efficient choice.
Flange maintenance
Flanges are easier to dismantle for inspection, especially in critical systems. In large industrial plants, flange systems simplify valve and pipeline replacement.
Pressure and Temperature: Where Flanges Usually Win
Couplings are suitable for medium pressure
Most couplings can handle medium pressure levels, but their performance is limited by gasket material and bolt strength.
Flanges excel in high-pressure environments
Flanges are the standard choice for high-pressure pipelines. Many flange types can handle pressures above 16 bar (PN16) and higher, depending on material and standard.
Material and Corrosion Resistance: Stainless Steel Benefits
Stainless steel coupling advantages
ss pipe coupling offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for water treatment, chemical, and marine applications.
Stainless steel flange advantages
Flanges made from stainless steel provide high corrosion resistance and strong structural stability, especially in corrosive or harsh environments.
Procurement Decision Guide: How to Choose
If your system needs quick installation
Choose ss pipe coupling to reduce labor and shorten project timelines.
If your system requires frequent inspection
Choose flanges for easy disassembly and maintenance.
If your system is high-pressure
Choose flanges to ensure stability and safety.
If your system is medium pressure and tight space
Choose couplings to save space and cost.
Engineering Standards and Compliance

Coupling standards
Couplings usually follow standards like ISO, ASTM, and DIN depending on type. Procurement must verify supplier certifications.
Flange standards
Flanges must comply with ASME B16.5, ISO 7005, EN 1092, and other standards. These standards ensure compatibility and safety.
Real-World Case Study: Coupling vs Flange Decision
A chemical plant in Southeast Asia replaced flanges with ss pipe coupling in a 500m pipeline section. The results were:
- Installation time reduced by 28%
- Labor cost reduced by 21%
- Leakage incidents reduced by 12% due to fewer welding joints
However, the plant kept flanges in high-pressure sections due to safety and inspection needs.
This example shows that a hybrid approach often provides the best balance.
Comparison Table: Coupling vs Flange (Detailed)
| Criteria | ss pipe coupling | Flange |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Speed | Faster, less labor | Slower, more labor |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Long-term Maintenance | Easier replacement | Easier inspection |
| Pressure Rating | Medium to high | High to very high |
| Temperature Rating | Moderate | High |
| Space Requirements | Compact | Larger footprint |
| Alignment Requirements | Flexible | Strict |
| Leakage Risk | Sensitive to installation | More stable if torque is correct |
| Best Use Case | Tight space, medium pressure | High pressure, frequent inspection |
| Typical Industries | HVAC, water, food | Petrochemical, power, high-pressure systems |
Common Mistakes When Choosing ss pipe coupling
Using wrong gasket material
Many leakage issues happen because the gasket material is incompatible with fluid. For example, NBR is not suitable for high temperature or chemical corrosion.
Ignoring torque requirements
Improper torque leads to uneven compression and leakage. Couplings require consistent torque across bolts.
Ignoring pipe alignment
Even though couplings are flexible, extreme misalignment will reduce sealing performance.
Common Mistakes When Choosing Flange
Incorrect gasket selection
Using wrong gasket can lead to leakage under high pressure.
Ignoring bolt torque
Bolt torque directly affects sealing performance. Under-torque or over-torque both cause issues.
Ignoring flange face type
Different flange face types (RF, FF, RTJ) must match gasket type and system pressure.
Procurement Checklist: How to Ensure Quality
Supplier qualifications
Choose suppliers with ISO certification and verified traceability.
Material verification
Verify material certificates (MTC) and confirm grade (304, 316, 316L, etc.).
Product inspection
Use third-party inspection for critical systems.
Documentation
Ensure the supplier provides complete documentation including test reports, material certificates, and installation guidelines.
How to Choose Between ss pipe coupling and Flange
Step 1: Confirm system pressure and temperature
If the system exceeds the rated limits of couplings, choose flanges.
Step 2: Evaluate maintenance needs
If frequent inspection is required, choose flanges.
Step 3: Evaluate installation environment
If space is tight or installation time is limited, choose couplings.
Step 4: Evaluate long-term cost
Consider total cost including downtime, maintenance, and potential leakage risks.
Conclusion
There is no absolute winner between ss pipe coupling and flange. The best choice depends on project requirements such as pressure, temperature, maintenance frequency, and installation environment. For procurement professionals, the most cost-effective approach often involves combining both methods: use couplings for medium pressure, tight space, and fast installation; use flanges for high-pressure, high-temperature, and inspection-intensive systems.
In modern industry, the most successful systems are those that match connection types to real-world conditions rather than relying on a single standard solution.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of ss pipe coupling?
The main advantage is fast installation and lower cost, especially suitable for medium-pressure piping systems.
Can ss pipe coupling handle high pressure?
Some high-pressure couplings can handle higher pressure, but flanges are generally more reliable for very high pressure systems.
Is flange better for safety?
In extreme conditions, flange connections provide higher safety due to stronger mechanical strength and more stable sealing.
Are couplings reusable?
Yes, couplings can be reused, but gaskets may need replacement.
Which is better for corrosion resistance?
Both can be made of stainless steel. Corrosion resistance depends on material grade and sealing material.
Can couplings be used for large diameter pipes?
Couplings can be used for larger pipes but are often limited by design. Flanges are more suitable for large diameter systems.






