Table of Contents
Introduction
Hydraulic line fittings are essential components of hydraulic systems, playing a crucial role in connecting hoses, tubes, and pipes while ensuring fluid flow. These fittings are designed to handle high-pressure environments, withstand harsh conditions, and prevent leaks. Understanding the different types of hydraulic line fittings is vital for engineers, system designers, and maintenance teams to make informed decisions when designing, installing, or maintaining hydraulic systems.
In this blog, we’ll explore the top 5 hydraulic line fitting types you should know. We will cover their applications, advantages, and considerations when selecting the appropriate fitting for your system. Whether you’re working with high-pressure systems, mobile machinery, or industrial equipment, knowing how to choose the right hydraulic fittings is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your hydraulic system.
1. Threaded Hydraulic Line Fittings
Threaded hydraulic line fittings are one of the most common types used in hydraulic systems. These fittings feature a threaded design, which allows them to be securely connected to hydraulic hoses, pipes, or other components. There are two main types of threaded hydraulic fittings: male and female threaded fittings.
Advantages of Threaded Hydraulic Line Fittings
- Ease of Installation: Threaded fittings are simple to install, requiring only a few turns to connect or disconnect the fitting.
- Versatility: These fittings are widely used in a variety of hydraulic systems, from low to high-pressure environments.
- Leak Resistance: When correctly installed, threaded fittings provide a tight seal, reducing the risk of leaks.
Applications of Threaded Hydraulic Line Fittings
Threaded fittings are ideal for applications that involve medium to high-pressure systems. They are commonly used in industries such as:
- Automotive
- Construction
- Manufacturing
- Aerospace
Considerations
When using threaded hydraulic fittings, it is important to choose the correct thread type and size. Using the wrong thread can lead to leaks or system failure. Additionally, proper tightening is crucial to prevent overtightening, which could cause damage to the fitting or system.
2. Quick-Connect Hydraulic Line Fittings

Quick-connect hydraulic line fittings, also known as quick-disconnect fittings, allow for rapid and easy connection and disconnection of hydraulic lines without the need for tools. These fittings are designed to minimize downtime and provide a safe and efficient way to connect hydraulic systems.
Advantages of Quick-Connect Hydraulic Line Fittings
- Fast Connection and Disconnection: These fittings allow operators to quickly connect or disconnect hydraulic lines, making them ideal for systems that require frequent maintenance or servicing.
- No Tools Required: Unlike traditional fittings, which require wrenches or other tools, quick-connect fittings can be operated by hand.
- Leak Prevention: Most quick-connect fittings have a built-in sealing mechanism that helps prevent leaks during connection or disconnection.
Applications of Quick-Connect Hydraulic Line Fittings
Quick-connect hydraulic fittings are commonly used in mobile machinery, construction equipment, and maintenance operations where frequent connection and disconnection are required. They are ideal for:
- Agricultural machinery
- Construction equipment
- High-mobility systems
Considerations
While quick-connect fittings provide convenience, they may not always be suitable for high-pressure applications. It’s important to verify the pressure rating and ensure that the quick-connect fitting is appropriate for the application.
3. Flanged Hydraulic Line Fittings
Flanged hydraulic line fittings use a flanged connection to join hydraulic pipes, tubes, or hoses. These fittings are often used in systems where high flow rates and pressure are required. Flanged fittings are typically bolted together, providing a secure and durable connection.
Advantages of Flanged Hydraulic Line Fittings
- High-Pressure Performance: Flanged fittings are ideal for high-pressure systems and can handle higher flow rates than threaded fittings.
- Strong and Durable: Flanged fittings provide a strong, durable connection, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- Sealing Flexibility: Flanged fittings can accommodate various sealing methods, including gaskets or o-rings.
Applications of Flanged Hydraulic Line Fittings
Flanged hydraulic fittings are commonly used in high-pressure systems in industries such as:
- Oil and gas
- Power generation
- Heavy-duty machinery
Considerations
Flanged fittings require careful alignment during installation. Improper alignment can cause misalignment of the flanges, leading to leaks or system failure. Additionally, flanged fittings may require more space than threaded or quick-connect fittings, which can be a consideration in compact systems.
4. Push-In Hydraulic Line Fittings
Push-in hydraulic line fittings, also known as push-to-connect fittings, allow for easy and quick connection of hydraulic lines without the need for tools. These fittings use a simple push mechanism to secure the hose or tube in place, providing a reliable connection with minimal effort.
Advantages of Push-In Hydraulic Line Fittings
- Easy Installation: Push-in fittings are easy to install, making them ideal for applications where rapid setup is essential.
- Space-Saving: These fittings are compact and can be used in tight spaces, making them suitable for systems where space is limited.
- Reusability: Many push-in fittings are reusable, which makes them cost-effective in the long run.
Applications of Push-In Hydraulic Line Fittings
Push-in hydraulic fittings are commonly used in systems that require quick, temporary connections. They are ideal for:
- Mobile equipment
- Agricultural machinery
- Industrial applications
Considerations
While push-in fittings are convenient, they may not be suitable for high-pressure or high-temperature environments. It’s important to verify the specifications of the push-in fitting to ensure it’s appropriate for the intended use.
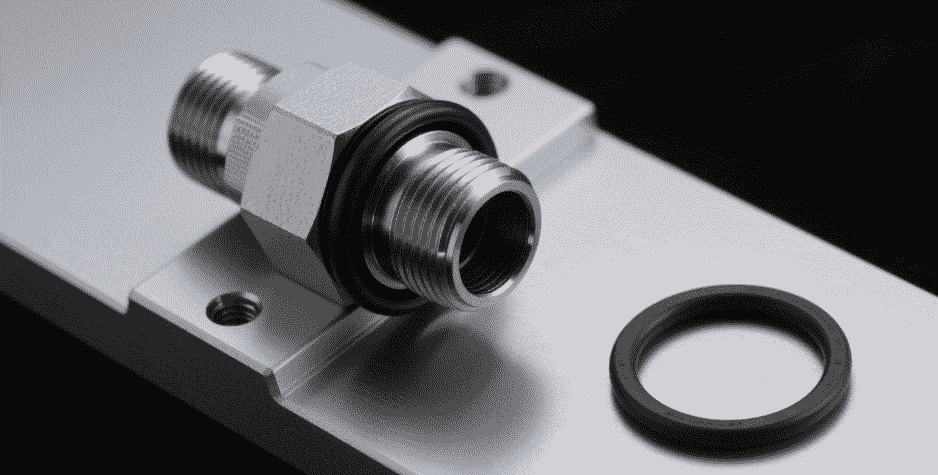
5. O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) Hydraulic Line Fittings
O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) hydraulic line fittings provide a reliable, leak-free seal using an o-ring placed on the face of the fitting. These fittings are designed to handle high-pressure environments and are commonly used in systems where a high degree of leak resistance is required.
Advantages of ORFS Hydraulic Line Fittings
- Leak Prevention: ORFS fittings provide a superior seal, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage.
- High-Pressure Capability: These fittings are capable of withstanding high pressures, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Durability: ORFS fittings are designed to last, even in harsh environments.
Applications of ORFS Hydraulic Line Fittings
ORFS hydraulic line fittings are commonly used in industries that require high-pressure, leak-free connections, including:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Heavy machinery
Considerations
ORFS fittings require precise installation to ensure the o-ring is seated correctly. Additionally, while ORFS fittings provide a reliable seal, they may not be as easy to disconnect as other fitting types.
Table: Comparison of Hydraulic Line Fitting Types
| Fitting Type | Advantages | Applications | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threaded Hydraulic Fittings | Versatile, leak-resistant, easy to install | Automotive, manufacturing, aerospace | Requires correct thread size, proper tightening |
| Quick-Connect Hydraulic Fittings | Fast connection, no tools needed, leak prevention | Mobile machinery, construction, agriculture | May not be suitable for high-pressure systems |
| Flanged Hydraulic Fittings | High-pressure performance, durable, strong seal | Oil & gas, power generation, heavy-duty machinery | Requires alignment, space-consuming |
| Push-In Hydraulic Fittings | Easy to install, compact, reusable | Mobile equipment, industrial, agricultural | Not suitable for high-pressure environments |
| ORFS Hydraulic Fittings | Leak-free, high-pressure capability, durable | Aerospace, automotive, heavy machinery | Requires precise installation, less easy to disconnect |
Conclusion
Selecting the right hydraulic line fittings is crucial for ensuring the performance, safety, and longevity of hydraulic systems. Each type of fitting has its own unique advantages and is suitable for different applications, from quick-connect fittings that save time on maintenance to threaded and flanged fittings designed for high-pressure systems.
When choosing hydraulic line fittings, it’s essential to consider factors such as the system’s pressure, flow rate, temperature, and the ease of installation and maintenance. By understanding the different types of hydraulic fittings and their applications, you can make an informed decision that meets your specific needs.
FAQ
Q1: What are the most common types of hydraulic line fittings?
A1: The most common types include threaded fittings, quick-connect fittings, flanged fittings, push-in fittings, and O-ring face seal (ORFS) fittings.
Q2: How do I choose the right hydraulic line fitting for my system?
A2: When selecting hydraulic line fittings, consider factors such as pressure ratings, temperature requirements, fluid compatibility, and ease of installation.
Q3: Are quick-connect hydraulic fittings suitable for high-pressure systems?
A3: While quick-connect fittings are convenient, they may not be suitable for all high-pressure applications. Always verify the pressure rating before selecting a quick-connect fitting.
Q4: Can I reuse push-in hydraulic fittings?
A4: Yes, many push-in hydraulic fittings are reusable, making them a cost-effective option for systems that require frequent changes or maintenance.
Q5: Why is leak prevention important in hydraulic systems?
A5: Leak prevention is crucial in hydraulic systems to ensure safety, maintain fluid integrity, and prevent environmental contamination or damage to equipment.
Q6: What materials are typically used for hydraulic line fittings?
A6: Hydraulic line fittings are commonly made from materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and aluminum. The material selection depends on the application’s pressure, temperature, and corrosion resistance requirements.
Q7: How can I prevent hydraulic fitting leaks?
A7: To prevent leaks, ensure that fittings are properly tightened, the correct seal materials are used, and fittings are installed according to manufacturer guidelines. Regular maintenance and inspection can also help detect potential issues early.
Q8: What is the difference between male and female threaded hydraulic fittings?
A8: Male threaded fittings have external threads, while female threaded fittings have internal threads. These are designed to connect with each other to form a secure and leak-proof seal in hydraulic systems.
Q9: How can I identify the right size for hydraulic line fittings?
A9: The size of hydraulic line fittings is determined by the inner and outer diameter of the tube or hose and the thread size. It’s essential to match the fitting size with the specifications of the hose or pipe to ensure a proper connection.
Q10: Are flanged hydraulic fittings more durable than threaded fittings?
A10: Yes, flanged hydraulic fittings are generally more durable than threaded fittings because they offer a higher level of sealing and are capable of handling higher pressure and flow rates, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.